Call For Paper
Pen & Prosperity
(eISSN-3048-9555)
INDEXED II OPEN ACCESS II PEER REVIEWED II REFEREED JOURNAL II MULTIDISCIPLINARY II QUARTERLY ll SCHOLARLY II INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL
We are a multidisciplinary journal; we welcome submissions from any and all areas of study in the following fields: engineering, mathematics, economics, social science, the arts, medicine, pharmacy, business administration (MBA), physical science, computer science, and all branches of the physical science.






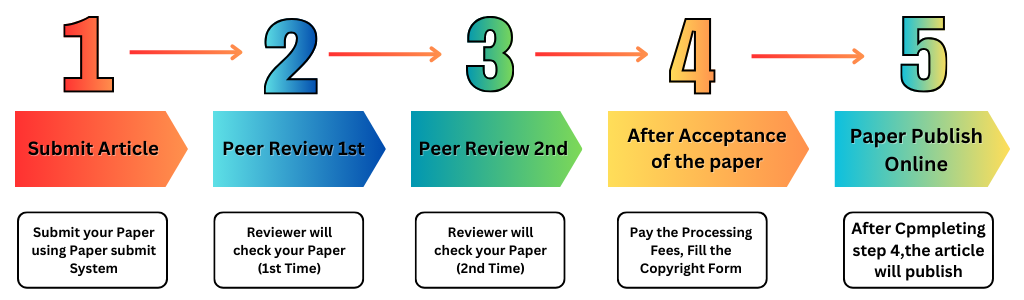
PUBLICATION PROCESS
Fllow this steps and publish your Research Paper
Current Issue
Author: Arijit Bera & Dr. Chaman Singh
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.70798/PP/020300001
Abstract: Professional development in multicultural workplaces is a critical component of fostering diversity, inclusion, and organizational growth. As globalization reshapes workforce demographics, organizations increasingly recognize diversity not merely as a demographic reality but as a source of innovation, creativity, and competitive advantage. Inclusive professional development programs go beyond traditional skill-building to emphasize cultural empathy, intercultural communication, and equity in career advancement. However, achieving this vision is complex, as cultural differences, structural barriers, and systemic inequalities often hinder progress. Research highlights the importance of cultural intelligence (CQ) as a key competency for navigating diverse environments and underscores the role of inclusive leadership in promoting psychological safety and belonging. Effective strategies such as mentorship, bias awareness training, employee resource groups, and flexible learning platforms ensure equitable access to growth opportunities. Moreover, emerging technologies like AI and VR, along with intersectional frameworks, are transforming the future of diversity and inclusion initiatives. This paper examines the challenges, strategies, and organizational impacts of multicultural professional development, arguing that sustainable inclusion frameworks are essential for cultivating global talent and fostering innovation. Ultimately, investing in inclusive professional development is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic necessity for organizations seeking long-term success in a culturally diverse world.
Keywords: Professional Development, Inclusive, Challenges, Strategies.
Page No: 1-8
Author: Asim Mahata & Dr. Chaman Singh
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.70798/PP/020300002
Abstract: The education of tribal girls represents one of the most pressing challenges in the pursuit of equitable and inclusive education systems in India. Despite significant policy reforms and constitutional safeguards, tribal communities continue to experience widespread educational deprivation due to structural inequalities, cultural marginalization, and entrenched socio-economic barriers. This theoretical study explores the interconnectedness of socio-economic status (SES) and familial dynamics in shaping the educational experiences and outcomes of tribal girls, with a particular focus on the secondary level. Drawing upon sociological theories, gender studies, and education research, it analyzes the role of poverty, cultural beliefs, gender norms, parental aspirations, and community engagement in influencing school enrollment, retention, and academic performance. The study argues for a culturally responsive and holistic approach to educational interventions, emphasizing economic empowerment, parental awareness, and the integration of indigenous knowledge systems. The findings contribute to a nuanced understanding of intersectional barriers while offering theoretical insights for policy formulation and community-based strategies aimed at promoting educational equity.
Keywords: Tribal Girls, Socio-Economic Status, Parental Aspirations, Cultural Marginalization, Educational Equity.
Page No: 9-14
Author: Barun Das
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.70798/PP/020300003
Abstract: Smart Learning Ecosystems (SLEs) represent a transformative approach to education, integrating Information and Communication Technology (ICT) innovations to create learner-centered, adaptive, and collaborative environments. This study explores the conceptual framework, theoretical underpinnings, and pedagogical implications of SLEs, emphasizing how digital learning platforms, artificial intelligence, immersive technologies, and mobile learning facilitate personalized learning, continuous assessment, and real-time feedback. By leveraging data-driven insights and interactive tools, SLEs enhance student engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention while promoting inclusivity and equitable access to education. The study also examines the role of SLEs in fostering lifelong learning, critical thinking, and 21st-century skills necessary for complex, dynamic knowledge societies. Findings highlight the potential of ICT-driven ecosystems to transform traditional education into a flexible, interconnected, and sustainable learning model. This research provides guidance for educators, policymakers, and institutions seeking to implement effective technology-enabled learning strategies.
Keywords: Smart Learning Ecosystems, ICT Innovations, Personalized Learning, Adaptive Learning, Educational Technology.
Page No: 15-21
Author: Pinaki Barmon & Dr. Chaman Singh
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.70798/PP/020300004
Abstract: Mobile learning (m-learning) and microlearning are revolutionizing education by offering flexible, personalized, and accessible learning experiences tailored to the demands of the digital age. This study examines the principles, integration, benefits, and challenges of these innovative approaches, emphasizing their transformative potential in reshaping traditional education systems. Mobile learning leverages smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices to enable learning anytime and anywhere, while microlearning delivers concise, targeted content designed to enhance engagement, retention, and practical application. Together, these strategies promote learner autonomy, bridge geographical and socio-economic gaps, and foster lifelong learning habits. The paper explores how interactive features, gamification, and just-in-time learning contribute to effective knowledge transfer, making education more relevant and performance-driven. Additionally, it identifies barriers such as digital inequality, content quality concerns, distraction risks, accreditation challenges, and data security issues, emphasizing the need for strategic planning, innovation, and inclusive policies. By synthesizing theoretical perspectives and practical implications, this study provides valuable insights for educators, policymakers, and instructional designers seeking to create dynamic, equitable, and future-ready educational ecosystems in an increasingly technology-driven world.
Keywords: Mobile Learning, Microlearning, Digital Education, Lifelong Learning, Instructional Design.
Page No: 22-30
Author: Khurshida Katun
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.70798/PP/020300005
Abstract: The Sundarbans of West Bengal had been recognized as one of the most flood-prone regions in India due to its unique geographical setting and ecological fragility. The area had frequently experienced tidal surges, embankment breaches, cyclonic storms, and heavy monsoonal rainfall, which had severely affected local communities. The present study had been undertaken to investigate the impact of flood hazards on livelihoods in the Sundarbans, particularly in the South 24 Parganas district. A structured questionnaire survey had been administered among 200 respondents across Gosaba, Basanti, and Sagar blocks. Data had been analyzed using descriptive statistics, ANOVA, and post hoc tests to identify demographic variations in perception and impact. The findings revealed that heavy rainfall (87%), embankment breaches (74%), and tidal surges (63%) had been reported as the primary causes of flooding. Livelihood disruptions had been most severe for farmers and fishermen, with significant differences across age, occupation, and education groups (p < 0.05). The study concluded that sustainable embankment management, livelihood diversification, and community-based disaster preparedness programs were essential for resilience-building in the Sundarbans.
Keywords: Sundarbans, Flood Hazard, Livelihood, South 24 Parganas, Coastal Vulnerability, Disaster Risk Reduction, Embankment Breach.
Page No: 31-39

